viernes, 25 de mayo de 2018
Lugares históricos
Los lugares emblemáticos de cada país están determinados por su historia. En
todo el mundo existen lugares que hablan de la vida y cultura de las sociedades,
sitios como pirámides, fuertes, catedrales, puentes, prisiones, entre otros, hablan
de camino de la humanidad a través del tiempo.
En muchos casos, las guerras o la necesidad de crear nuevas construcciones han
hecho que los vestigios arquitectónicos desaparezcan. A pesar de esto, aún es
posible conocer muchos de estos lugares.
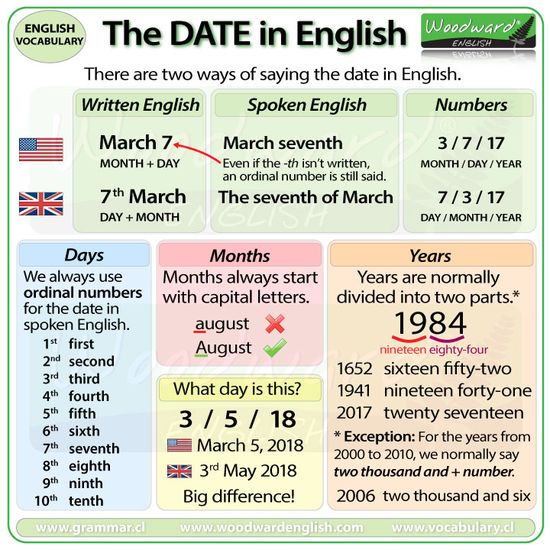
Ejemplos:
• Alcratraz Island was a prison. It is located in San Francisco Bay.
• We had lunch at Luxembourg gardens.
• Mayan temples are impressive.
• St. Paul’s Cathedral is in London.
Completa los espacios en blanco con los verbos en pasado
simple.
My friend Alex lives in London. Last year, I…………………………… (visit) him and he
…………………………… (take) me to visit the city. The first day we _______ (go) to
Buckingham Palace. I……………………… (not see) the Queen! Then we went to Trafalgar
Square and……………………… (feed) the pigeons. After lunch we………………………… (go) to the
National History Museum and we …………………………… (stay) there all afternoon.
On Sunday morning we………………………… (go) to see Big Ben. After lunch we…………………………
(go) to the Tower of London. At the end of the afternoon we………………………… (be) tired.
We………………………… (go) back to Alex’s house.
Visita al museo
Lee lo que menciona una guía en el museo de Crystal Bridges, en Arkansas, EE.UU.
In the museum a guide is speaking:
“Welcome to Crystal Bridges Museum. In this museum we
have some permanent American paintings and some paintings
that belong to other museums just for a period of time. All
the paintings you see here, belong to contemporary art, so
we don’t have any ancient paintings in the museum. We have
some paintings of Winslow Homer, and Arthur Fitzwilliam Tait’s,
Jasper Johns, to name a few painters. Please enjoy the tour”.
Entra al sitio del museo y ve qué exposiciones exhiben actualmente:
http://crystalbridges.org/
PERSONAJES IMPORTANTES DEL PASADO HABLAR DE ELLOS
What was her name?
Her name was Marie Curie
What did she do?
She was a scientist and she discovered
radiation.
Did she win any important prize?
Yes, she did. She won two Nobel prizes.
Did she become a university professor?
Yes, she became the first woman professor at
the University of Paris.
How did she influence world science?
Her research influenced medical knowledge
and disease treatment.
Why did she die?
She died because of exposure to radiation.
Expresión del tiempo: preposiciones y adverbios
At Se usa para expresar la hora o momento
en el que sucedió un evento.
• at nine o’clock.
• at a time EXAMPLE:At • Independence movement started at midnight.
• She became professor at a time when only men did.
In Se usa para expresar un periodo de
tiempo en el que sucedió un evento:
mes, año, década, siglos y estaciones
del año.
• In September
• In 1980
• in the 1950s.
• In 15th century
• In winter EXAMPLE: In • She was born in the 19th century, in 1815.
• The social movement started in September.
On Se usa para indicar una fecha precisa
o un día de la semana.
• On Sunday
• On February 14th, 1980 /
On 14 February 1980 EXAMPLE: On • She was born on May 10th, 1954.
During Se usa para expresar el
intervalo de tiempo en el que ocurrió
una acción en relación con otro evento
de mayor duración.
• During the year.
• She moved to Paris during
the war.
• The economy was weak
during the 1990s
Ago Se usa para indicar el paso de un
periodo de tiempo.
• A long time ago
• Centuries ago
• Decades ago
• Years ago EXAMPLE: Ago • Women got political participation decades ago.
• Mexico City experienced an earthquake years ago.
Last Se usa para indicar el último
periodo.
• Last year
• Last decade
• Last century Ejemplos: Last • Camarena invented Coler TV last century.
• Smartphones became popular last decade
***************************************************
VOCABULARIO PERSONAJES DE LA HISTORIA
FIGURES OF HISTORY
|
|||
|
ARTIST
|
ARTISTA
|
LEADER
|
LIDER
|
|
CITIZEN
|
CIUDADANO
|
MUSICIAN
|
MUSICO
|
|
INVENTOR
|
INVENTOR
|
NAVIGATOR
|
NAVEGADOR
|
|
RESEARCH
|
INVESTIGAR
|
PAINTER
|
PINTOR
|
|
JOURNALIST
|
PERIODISTA
|
PHILOSOPHER
|
FILOSOFO
|
|
KING
|
REY
|
PRESIDENT
|
PRESIDENTE
|
|
QUEEN
|
REINA
|
SCIENTIST
|
CIENTIFICO
|
|
SOLDIER
|
SOLDADO
|
THINKER
|
PENSADOR
|
|
EXPLORER
|
EXPLORADOR
|
ASTROLOGER
|
ASTROLOGO
|
Ejemplos:
• Frida Kalho was a famous surrealistic Mexican painter.
• The scientist and artist Leonardo da Vinci dedicated his life to develop new inventions.
• Richard I, King of England, was a great military leader and warrior. He was
also known as “Richard Lionheart”.
• Ludwig van Beethoven was a musician born in Vienna in 1770.
• Navigator Christopher Columbus discovered the Americas on an expedition
sponsored by Queen Isabella I in 1492.
Ejemplos:
• He was a famous philosopher in the 18th century
• The nineteenth century had significant
developments in mathematics, physics.
• His first year as a King was very difficult.
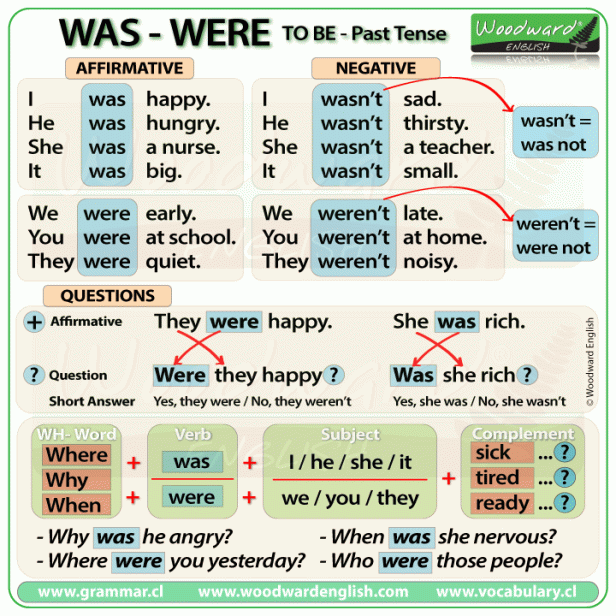
https://aprendamosmashoy.wordpress.com/2017/01/25/was-were-pasado-verbo-to-be/
QUESTIONS mod 7 sem 2
Preguntas:
El objetivo de la unidad es proporcionarte herramientas para que logres compartir
información relevante sobre diferentes eventos históricos.
Indicadores
Hablaremos del pasado y aprenderás a formular preguntas con el fin de obtener
información específica sobre los acontecimientos de la historia y experiencias
vividas por personajes del pasado. Identificarás y utilizaras las funciones del
lenguaje, las nociones gramaticales y vocabulario que te permitan expresar
cambios en el entorno, familiar, local, estatal, nacional y mundial .
Recuerda que utilizamos el pasado simple para referirnos a acciones que
sucedieron en un momento específico en el pasado, un aspecto importante a
considerar es el tipo de verbo que se usa en las oraciones.
Para hacer preguntas en inglés se usan dos formas básicas:
- Preguntas que comienzan con el auxiliar Did
- Preguntas específicas con palabras Wh,
Veamos la estructura de las preguntas en las dos formas:
NEGATIVE verbo
El objetivo de la unidad es proporcionarte herramientas para que logres compartir
información relevante sobre diferentes eventos históricos.
Indicadores
Hablaremos del pasado y aprenderás a formular preguntas con el fin de obtener
información específica sobre los acontecimientos de la historia y experiencias
vividas por personajes del pasado. Identificarás y utilizaras las funciones del
lenguaje, las nociones gramaticales y vocabulario que te permitan expresar
cambios en el entorno, familiar, local, estatal, nacional y mundial .
Recuerda que utilizamos el pasado simple para referirnos a acciones que
sucedieron en un momento específico en el pasado, un aspecto importante a
considerar es el tipo de verbo que se usa en las oraciones.
Para hacer preguntas en inglés se usan dos formas básicas:
- Preguntas que comienzan con el auxiliar Did
- Preguntas específicas con palabras Wh,
Veamos la estructura de las preguntas en las dos formas:
Simple Past Tense / Affirmative
El pasado simple se forma añadiendo la terminación "-ed" al verbo regular, y es la misma forma para todas las personas gramaticales.
Ejemplo:
REGULAR VERBS = Verb + ed or d
|
VERBOS REGULARES = Verbo + ed o d
|
I studied on Saturday.
I didn't study on Sunday. |
Estudié el sábado.
No estudié el domingo. |
You studied on Saturday.
You didn't study on Sunday. |
Estudiaste el sábado.
No estudiaste el domingo. |
She worked on Saturday.
She didn't work on Sunday. |
Trabajó el sábado.
No trabajó el domingo. |
He exercised on Saturday.
He didn't exercise on Sunday. |
Hizo ejercicio el sábado.
No hizo ejercicio el domingo. |
We exercised on Saturday.
We didn't exercise on Sunday. |
Hicimos ejercicio el sábado.
No hicimos ejercicio el domingo. |
They exercised on Saturday.
They didn't exercise on Sunday. |
Hicieron ejercicio el sábado.
No hicieron ejercicio el domingo. |
Simple Past Tense / Negative
En su forma negativa, el verbo principal mantiene su forma infinitiva, el auxiliar do, en su forma pasada (didn´t) es el verbo que define el pasado de la frase.
Simple Past Tense / Questions
Al formular una pregunta, también el verbo principal mantiene su forma infinitiva (invent), el auxiliar do, en su forma pasada (did), es el verbo que define el pasado de la pregunta.
|
QUESTIONS
|
|||
|
AUXILIARY
|
PRONOUNS
|
VERB
|
COMPLEMENT
|
|
DID
|
I
YOU
HE/ SHE
WE
YOU
THEY
|
INVENT
|
THE FIRST AIRCRAFT?
|
ANSWER SHORT (RESPUESTAS CORTAS) _________________________________________________________________
I,You
He/she
No We,You didn´t = did not work
They
__________________________________________________________________
AFIRMATIVE
AFIRMATIVE
I,You
He/she
YES We,You did work
They
*********************************************************************
PRACTICAR ➤AQUI
sábado, 19 de mayo de 2018
SIMPLE PAST TENSE
Simple past
Para hablar de actividades o sucesos que se realizaron en el pasado y concluyeron en un momento específico en el pasado, usamos el pasado simple (past simple).
Examples:
Examples:
- • I lived in Mexico for a year. ([Yo] Viví en México por un año.)
• You ate vegetables two hours ago. ([Tú] Comí verduras hace dos horas.)
• She walked at the park this morning. ([Ella] Caminó en el parque esta mañana.)
• We drank water before leaving the house. ([Nosotros] Bebimos agua antes de salir de la casa.)
Regular verbs
Para formar el pasado simple, es importante que sepas que en inglés existen dos tipos de verbos: los regulares y los irregulares.
Para los verbos regulares solamente agregamos “ed” al final del verbo. En la siguiente tabla te colocamos algunos de los verbos regulares más comunes, pon mucha atención a la pronunciación:
Para los verbos regulares solamente agregamos “ed” al final del verbo. En la siguiente tabla te colocamos algunos de los verbos regulares más comunes, pon mucha atención a la pronunciación:
Regular
verbs
Infinitive Past simple Meaning
Answer Answered Responder
Ask Asked
Preguntar
Brush Brushed Cepillar
Clean Cleaned Limpiar
Close Closed Cerrar
Cook Cooked Cocinar
Dance Danced Bailar
Help Helped Ayudar
Listen Listened Escuchar
Live Lived Vivir
Love Loved Amar
Need Needed Necesitar
Open Opened Abrir
Play
Played Jugar/Tocar un instrumento/
actuar
Travel Traveled Viajar
Visit Visited Visitar
Wash Washed Lavar
Watch Watched Ver
Nota:En los verbos como love, close y live que terminan en “e” solamente se agrega la “d”: loved, closed, lived.
En los verbos monosílabos o con sílaba tónica al final que terminan con una sola vocal de sonido corto y cualquiera de las siguientes consonantes: b, d, g,l,m,n,p,r,t, se debe “doblar” la consonante al agregar “ed”. Observa los siguientes ejemplos:
Regular verbs
Verb Past Form Meaning
rob robbed robar
bid bidded ofertar
beg begged rogar
control controlled controlar
slam slammed cerrar de golpe, azotar
plan planned planear
stop stopped parar, detenerse
prefer preferred preferir
Los verbos listen, happen, honor y sufer no doblan consonante pues su sílaba tónica es en la primera sílaba. Sin embargo, en inglés británico puedes encontrar travelled, cancelled con doble ele.
Si el verbo termina con una consonante y una “y” como cry (llorar), se sustituye la “y” por una “i” y se agrega “ed”. Revisa la tabla con algunos ejemplos de este caso:
Verb Past Form Meaning
apply applied aplicar
cry cried llorar
copy copied copiar
fry fried freir
falsify falsified falsificar
hurry hurried apurarse
modify modified modificar
qualify qualified calificar
reply replied responder
spy spied espiar
supply supplied proveer
try tried tratar, intentar
Irregular verbs
Los verbos irregulares cambian por completo su estructura en pasado, observa la siguiente tabla con los verbos irregulares más comunes:
Infinitive Past Meaning
Be Was / were Ser / estar
Begin Began Comenzar
Bite Bit Morder
Break Broke Romper
Buy Bought Comprar
Draw Drew Dibujar
Drink Drank Beber
Drive Drove Manejar
Fight Fought Pelear
Go Went Ir
Make Made Hacer
Read Read Leer
Run Ran Correr
Sleep Slept Dormir
Speak Spoke Hablar
Swim Swam Nadar
Wear Wore Vestir
Win Won Ganar
Write Wrote Escribir
Te recomendamos buscar cada verbo en el traductor de Google para practicar su pronunciación: https://translate.google.com/?hl=es
Nota:
Algunos verbos aceptan tanto una forma regular como una irregular, y su uso depende del país angloparlante en el que estemos:
Infinitive Past regular form Past irregular form Meaning
learn learned (BR, Am) learnt (BR) aprender
burn burned burnt quemar
dream dreamed dreamt soñar
spell spelled spelt deletrear/escribir
Negatives and Questions
Para decir que alguien no hizo algo en el pasado, usamos el auxiliar did, y el verbo en infinitvo, por ejemplo, para decir, “Yo no viví en México por un año.” diríamos: I didn’tlive in México for a year . En pasado, no hay distinción para la tercera persona del singular (he, she, it). Es decir, si quisiéramos decir, “Ella no caminó en el parque esta mañana”, diríamos She didn’t walk at the park this morning. Observa la siguiente tabla con las estructuras para negar en pasado:
Subject Auxiliary verb Main verb in infinitve Complement
I did not live in México for a year.
didn´t
She did not
walk at the park this morning.
didn´t
De igual manera, para hacer preguntas, se usa el auxiliar did y se invierten el sujeto y el verbo. De modo que si quisiéramos decir “¿Tú viviste en México por un año?”, diríamos: Did you live in Mexico for a year?. Observa la estructura para construir preguntas:
Auxiliary verb Subject Main verb in infinitve Complement
Did you live in México for a year?
Did she walk at the park this morning?
Como posibles respuestas a las preguntas tenemos:
• Yes, she did.
• No, she didn’t.
Puedes practicar el uso del pasado simple en la siguiente liga:
http://learnenglishteens.britishcouncil.org/grammar-vocabulary/grammar-videos/past-simple-regular-verbs
Presente Progresivo. Present Progressive
MODULO 7 SEMANA 1
Affirmative form - Forma afirmativa
Formed by
Se forma con el:
Sujeto + am/is/are + Forma simple del verbo + terminación ing
= (S+am/is/are+SFV+ing)
Nota: Aquí se usa el verbo to be en presente y de acuerdo al sujeto:
*para I usamos “am”;
*para he, she, it usamos “is”, y
* para you, we, they usamos “are”.
Example:
• You are watching TV.
Interrogative form - Forma interrogativa
Formed by
Se forma con:
Am,Is, Are + Sujeto + Forma simple del verbo + terminación ing ?
NOTA: Aquí se usa el verbo to be en presente y de acuerdo con el sujeto:
*para I usamos “am”;
*para he, she, it usamos “is”, y
*para you, we, they usamos “are”.
Example:
• Are you watching TV?
Negative form - Forma negativa
Formed by
Se forma con:
Sujeto + am/is/are + not + Forma simple del verbo + terminación ing
Nota: Aquí se usa el verbo to be en presente y de acuerdo al sujeto:
*para I usamos “am”;
* para he, she, it usamos “is”,
*para you, we, they usamos “are”.
Example:
• You are not watching TV
 USE 1. Now - USO 1. Ahora
USE 1. Now - USO 1. Ahora
Use the Present Progressive/ Continuous with Normal Verbs to express the idea that something is happening now, at this very moment. It can also be used to show that something is not happening now.
Lo usamos para expresar la idea de que algo sucede en el mismo momento en que lo expresamos. También se usa para expresar que algo no está sucediendo ahora mismo, en su forma negativa.
Examples:
• You are learning english now.
• You are not swimming now.
• Are you sleeping?
• I am sitting.
• I am not standing.
• Is he sitting or standing?
• They are reading their books.
• They are not watching television.
• What are you doing?
• Why aren't you doing your homework?
USO 2. Acciones que se siguen llevando a cabo, que están en progreso.
In english, "now" can mean: this second, today, this month, this year, this century, and so on. Sometimes, we use the Present Continuous to say that we are in the process of doing a longer action which is in progress; however, we might not be doing it at this exact second.
En inglés “now” que es “ahora” significa en este mismo segundo, hoy, este mes, esta semana, este siglo. Depende del contexto. Lo usamos para decir que estamos en el proceso de estar haciendo algo, de tener una acción en proceso, sin embargo puede ser posible que en este segundo no la hagamos.
Examples: (All of these sentences can be said while I´m having dinner in a restaurant…)
Ejemplo: (Todos los siguientes enunciados pueden ser usados mientras estoy cenando en un restaurante…)
• I am studying to become a doctor.
• I am not studying to become a dentist.
• I am reading the book Tom Sawyer.
• I am not reading any books right now.
• Are you working on any special projects at work?
• Aren't you teaching at the university now?
STORY
Who are they? Where are they? What are they doing?
Right now, it is 10 o’clock Monday morning. Mike and Tina are at home. They are sitting at a table. They are eating breakfast.
At this moment, Tina is drinking coffee. She is eating a pastry. She is sitting across the table from Mike. She is talking to Mike.
Mike is Tina's husband. He is sitting at the table with Tina. He is also drinking coffee. Mike is listening to Tina.
After breakfast, Mike and Tina are leaving for work. They work in the city. They are riding the bus to work.
A continuación puedes revisar la estructura de las siguientes preguntas con sus respuestas:
1.- What time is it?
It’s ten o’clock.
2.- Is it Monday?
Yes, it is.
3.- What are Mike and Tina doing?
They are eating breakfast.
4.- What is Tina drinking?
She is drinking coffee.
5.- What is Mike doing?
He is cooking breakfast.
MATERIAL DE LA PLATAFORMA-Última modificación: martes, 16 de mayo de 2017, 17:59
REGULAR VERBS
Nociones gramaticales / verbos regulares
Es importante que sepas que en inglés existen dos tipos de verbos los regulares y los irregulares; a continuación podrás observar las tablas de verbos y escuchar su pronunciación. Revísalos las veces que consideres necesario y practica la pronunciación.
verbos regulares
Observa la siguiente tabla con los verbos regulares más comunes: ompersonal AQUI
verbos regulares
| Presente | Significado |
|---|---|
| Answer | Responder |
| Ask | Preguntar |
| Brush | Cepillar |
| Clean | Limpiar |
| Close | Cerrar |
| Dance | Bailar |
| Help | Ayudar |
| Learn | Aprender |
| Listen | Escuchar |
| Need | Necesitar |
| Open | Abrir |
| Play | Jugar/Tocar ( un instrumen |
Nociones gramaticales / verbos irregulares
Tabla verbos irregulares:
Presente Significado
Be Ser / estar
Bite Morder
Break Romper
Buy Comprar
Draw Dibujar
Drink Beber
Drive Manejar
Fight Pelear
Go Ir
Make Hacer
Read Leer
Run Correr
Sleep Dormir
Speak Hablar
Swim Nadar
Wear Vestir
Win Ganar
Write Escribir
Ahora que ya estudiaste los verbos regulares e irregulares es momento de conocer cómo los aplicamos en diferentes tiempos.
Simple Present Tense / Estructura gramatical del presente simple
SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE: AUXILIAR DO/DOES
|
|
AFFIRMATIVE:
|
I OPEN THE DOOR
HE OPENS THE DOOR
|
NEGATIVE:
|
I DON´T OPEN THE DOOR
HE DOESN´T OPEN THE DOOR
|
INTERROGATIVE: YES/NO
|
DO I OPEN THE DOOR?
DOES HE OPEN THE DOOR?
YES, I DO / NO I DON´T
YES, HE DOES / NO, HE
DOESN´T
|
Utilizamos el presente simple para hablar de actividades que hacemos de manera cotidiana (hábitos). Ejemplos:
I live in Mexico. ( Yo vivo en México. )
You eat vegetables. ( Tú comes vegetales. )
We drink water everyday. ( Nosotros bebemos agua todos los días. )
Observa que para una oración afirmativa en los sujetos He, She, It; debes agregar una “s” al final del verbo.
• En una oración negativa utilizamos “doesn’t” para los sujetos He, She, It mientras que utilizamos “don’t” para los sujetos I, You, We, They.
• Finalmente, observa que en caso de una interrogación (pregunta) utilizamos el auxiliar “does” para los sujetos He, She, It mientras que utilizamos “do” para los sujetos I, You, We, They.
Para hablar de actividades o sucesos que se realizaron y concluyeron en un momento específico en el pasado, usamos el pasado simple (past simple).
Examples:
• I lived in Mexico for a year. ([Yo] Viví en México por un año.)
• You ate vegetables two hours ago. ([Tú] Comiste verduras hace dos horas.)
• She walked at the park this morning. ([Ella] Caminó en el parque esta mañana.)
• We drank water before leaving the house. ([Nosotros] Bebimos agua antes de salir de la casa.)
Pasado Simple
⇩͢͢͢͢͢͢͢͢͢͢ ---------------------------------⟼
Past Present Future
3.1 Estructura gramatical Para formar el pasado simple, es importante que sepas que en inglés existen dos tipos de verbos: los regulares y los irregulares.
Para los verbos regulares solamente agregamos “ed” al final del verbo.
Regular verbs
Infinitive Past simple Meaning
Answer Answered Responder
Ask Asked Preguntar
Brush Brushed Cepillar
Clean Cleaned Limpiar
Close Closed Cerrar
Cook Cooked Cocinar
Dance Danced Bailar
Help Helped Ayudar
Listen Listened Escuchar
Ask Asked Preguntar
Brush Brushed Cepillar
Clean Cleaned Limpiar
Close Closed Cerrar
Cook Cooked Cocinar
Dance Danced Bailar
Help Helped Ayudar
Listen Listened Escuchar
En los verbos monosílabos o con sílaba tónica al final que terminan con una sola vocal
de sonido corto y cualquiera de las siguientes consonantes: b, d, g,l,m,n,p,r,t, se debe
“doblar” la consonante al agregar “ed”. Observa los siguientes ejemplos:
rob robbed robar
bid bidded ofertar
beg begged rogar
Si el verbo termina con una consonante y una “y” como cry (llorar), se sustituye la “y” por una “i” y se agrega “ed”. Revisa la tabla con algunos ejemplos de este caso:
Infinitive Past simple Meaning
apply applied aplicar
cry cried llorar
copy copied copiar
fry fried freir
falsify falsified falsificar
rob robbed robar
bid bidded ofertar
beg begged rogar
Si el verbo termina con una consonante y una “y” como cry (llorar), se sustituye la “y” por una “i” y se agrega “ed”. Revisa la tabla con algunos ejemplos de este caso:
Infinitive Past simple Meaning
apply applied aplicar
cry cried llorar
copy copied copiar
fry fried freir
falsify falsified falsificar
A nuestro favor, la mayoría de los verbos ingleses son 'regulares'. Esto significa que podemos confiar en las formas que adoptan porque siguen un patrón predecible. Aquellos verbos que no siguen las reglas básicas se llaman 'irregulares' y puedes consultarlos pulsando aquí.
|
La mayoría de los verbos de esta lista agregan "-d" o "-ed" al infinitivo. Los verbos resaltados en esta lista duplican su consonante final (admit - admitted) o cambian "-y" por "-ied", cuando la "y"está precedida por una consonante (bury - buried).
|
Suscribirse a:
Comentarios (Atom)





